Longer interval between maternal RSV vaccination and birth increases placental transfer efficiency
TAP was employed to collect capillary blood from 2-month-old infants for antibody tests of RSV and pertussis toxin.
Read More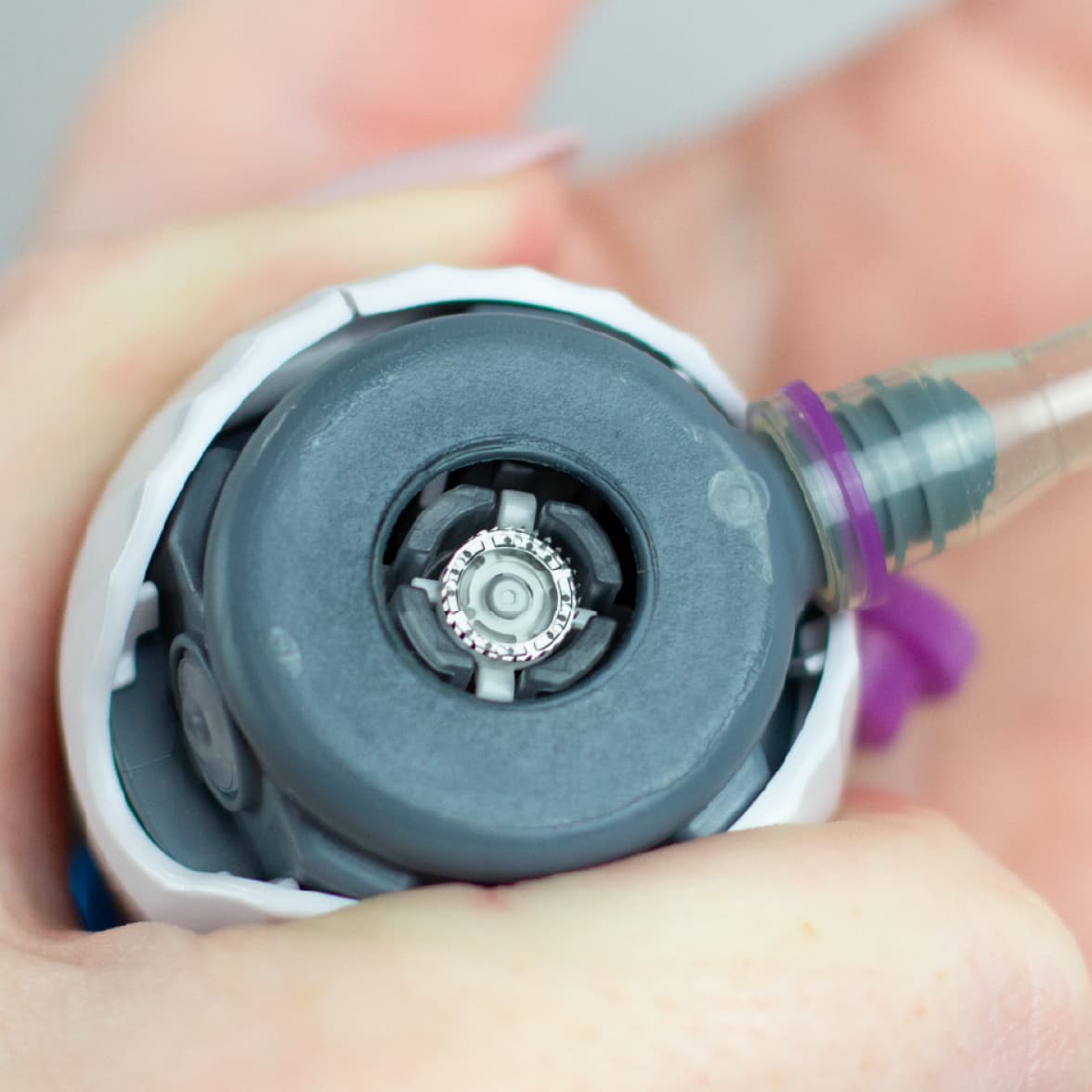
The Patented Bladeless Microneedle Array
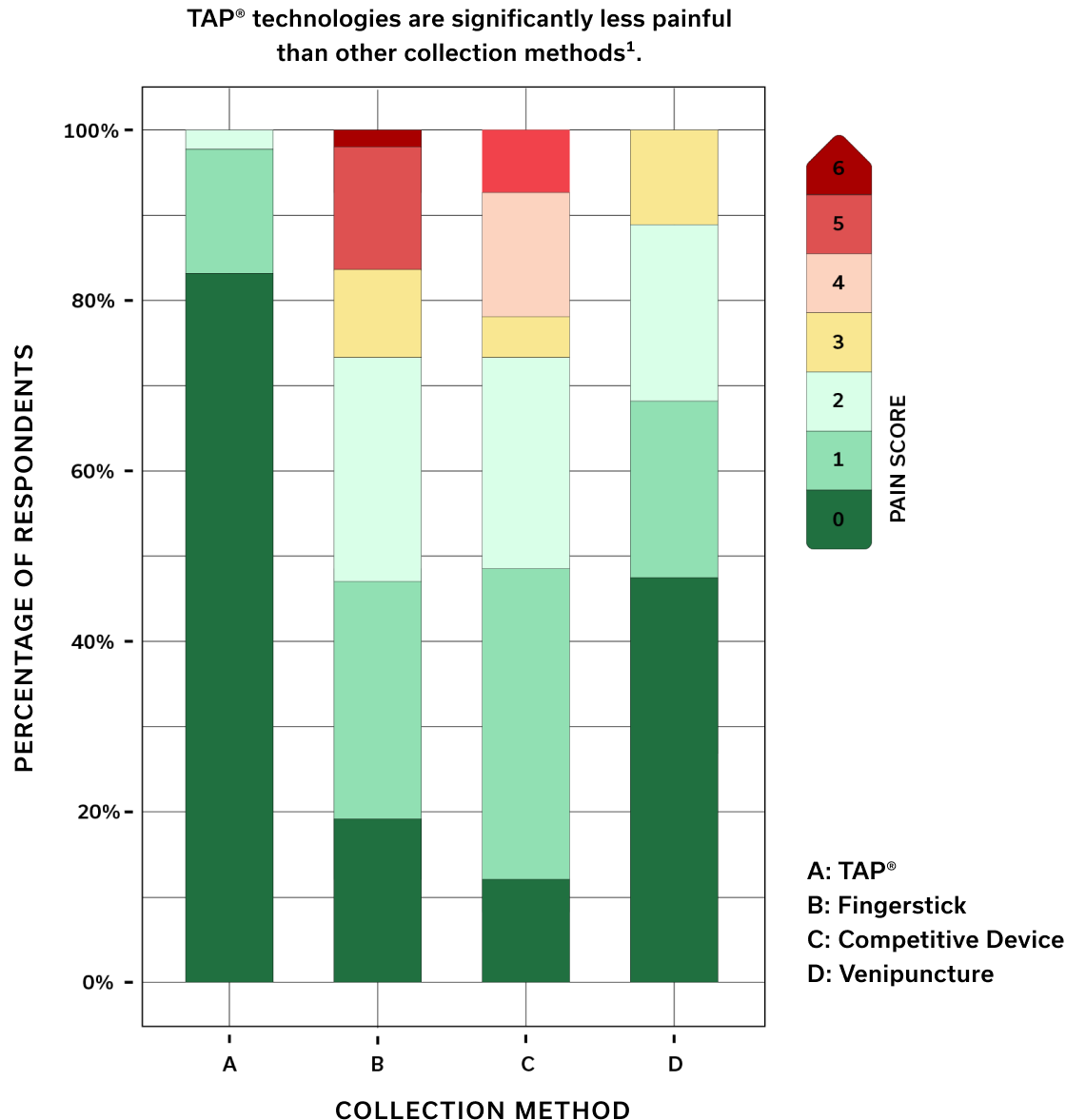
The bladeless microneedle array of our HALO™ technology overcomes these barriers. With microneedles thinner than an eyelash, HALO™ technology enables our TAP® devices to deliver a virtually painless blood collection experience compared to fingerstick, venipuncture, and competitive products.